INSEMINATION (INTRAUTERINE INSEMINATION)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a method used in infertility treatment. The IUI method is less invasive and more economical than in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment. However, a detailed medical evaluation should be performed to determine whether it is suitable for each couple.
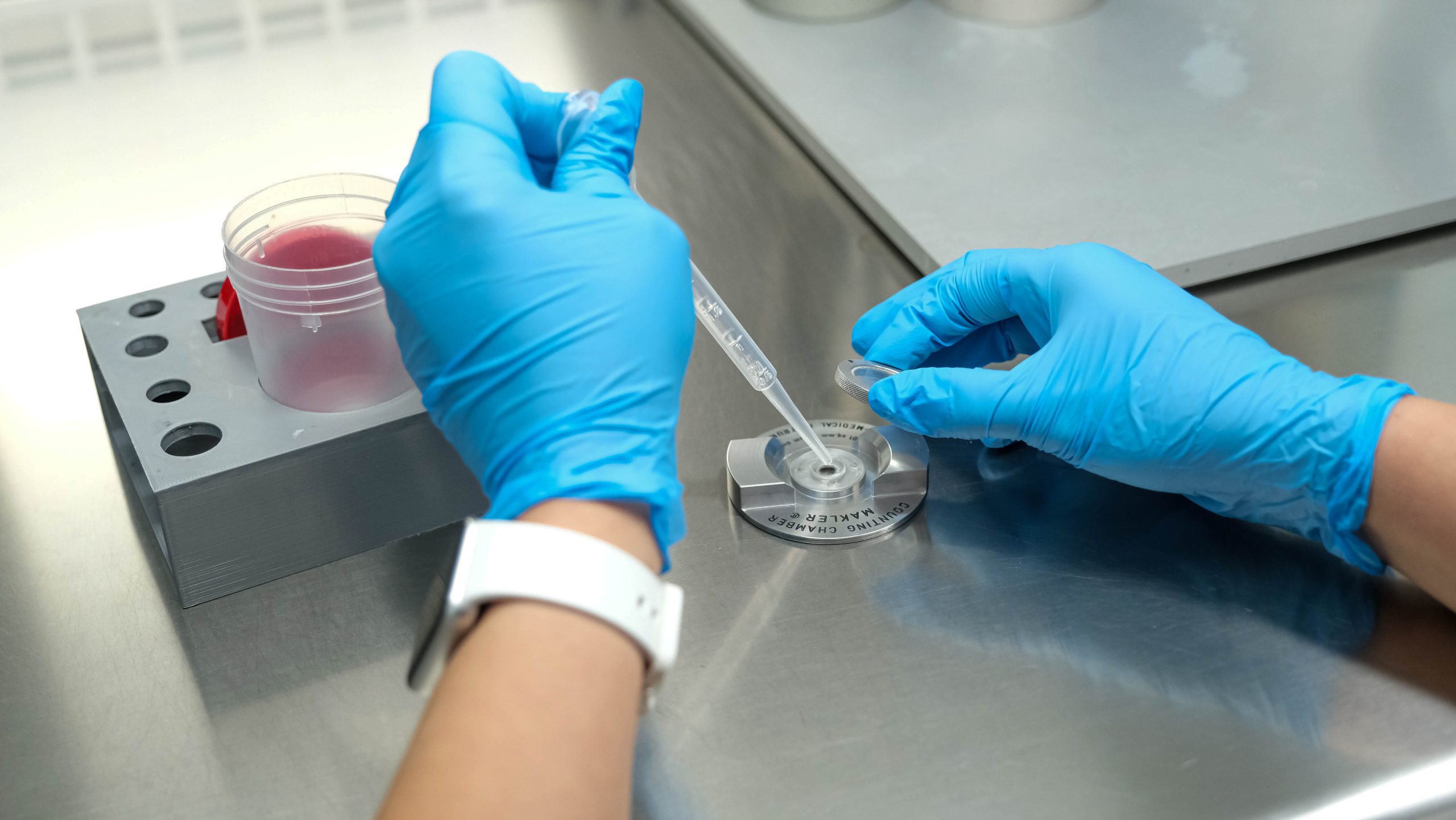
In this procedure, sperm cells are washed and concentrated in a laboratory setting, then placed directly into the uterus. IUI aims to increase the chances of fertilization by placing the sperm closer to the egg.
Situations in which IUI is used:
-
Low sperm count or motility: When a man has low sperm count or sperm motility problems.
-
Cervical (uterine) issues
-
Unexplained infertility When the cause of infertility cannot be identified.
-
Ovulation disorders When a woman has irregular ovulation or anovulation.
IUI process
-
Process: Women’s ovulation cycles are monitored. Egg-stimulating treatments are started on the 2nd or 3rd day of the menstrual cycle, either orally or through injections. Medications may be used to time ovulation.
-
Sperm preparation: The sperm sample collected from the male is washed in the laboratory, and the highest quality sperm cells are selected. If necessary, additional methods such as microfluidic chips can be used to sort sperm based on motility and morphology.
-
Insemination The sperm is placed inside the uterus using a thin catheter.
IUI is generally a painless procedure and is completed quickly. Success rates can vary depending on the couple’s age, the cause of infertility, and other factors.
If you want more information about this method or have specific questions, please contact a gynecologist.